What Neuromarketing is?
Neuromarketing is an innovative discipline that combines marketing and neuroscience. This field of study analyzes how consumers’ brains react to various marketing stimuli, such as advertising, packaging and products. Using advanced technologies such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalogram (EEG), researchers can directly observe brain responses.
The main goal of neuromarketing is to better understand the desires and motivations of consumers to improve marketing strategies. Thanks to this discipline, companies can create more effective advertising campaigns and products that better meet the needs of the market.
The fundamental principles
Neuromarketing is based on some fundamental principles that help understand how consumers make decisions. First of all, he recognizes that many buying decisions are driven by emotions, rather than logical reasoning. Our brain often reacts instinctively to stimuli, and these reactions affect what we buy.
Another key principle is that the human brain responds better to simple and clear messages. When a message is too complicated, our brain tends to ignore it. Therefore, marketing campaigns need to be direct and easily understandable.
This type of marketing also exploits the importance of the senses in the decision-making process. For example, bright colors, pleasant sounds and interesting textures can make a product more attractive. In addition, past memories and experiences play a crucial role. Positive past experiences increase the likelihood of consumers choosing the same brand again.
In addition, neuromarketing recognizes the power of repetition. When we see a message or product repeatedly, our brain considers it more familiar and reliable. These principles help in crafting marketing strategies that deeply engage consumers, significantly influencing their purchasing decisions.
Differences with classic marketing
Neuromarketing differs from traditional marketing primarily for its scientific, neuroscience-based approach. In traditional marketing, decisions are often based on surveys, focus groups, and market analysis that collect opinions stated by consumers. These methods can be useful, but they do not always reflect what consumers really think, as responses can be influenced by various factors, such as social desirability or the inability to properly express their emotions and motivations.
Neuromarketing, on the other hand, uses advanced technologies to directly observe the brain’s reactions to certain marketing stimuli. Instruments such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalogram (EEG) allow you to see which areas of the brain are activated in response to an advertisement, product or brand. This provides a more accurate and deeper view of the real preferences and motivations of consumers, going beyond what they can say in a survey.
The benefits of neuromarketing
The benefits of neuromarketing are many. First of all, it allows companies to create more effective advertising campaigns. Knowing the emotional reactions of consumers, it is possible to design messages that resonate better with the target audience. In addition, can help improve the design of products and packaging, making them more attractive and able to stimulate the right emotions.
Another advantage is the ability to optimize the consumer experience. For example, details about the arrangement of products in stores or the organization of websites can be refined to make the purchase process more intuitive and enjoyable. It can also reduce the risk of launching campaigns or products that do not resonate with the public, saving time and resources.
Social and commercial applications
Neuromarketing has numerous applications in both social and commercial fields. In the commercial field, companies can use these techniques to improve their advertising campaigns, making messages more effective and persuasive. For example, by analyzing brain reactions to the different elements of an ad, it is possible to determine which images, colors or words capture the most attention and arouse positive emotions. Additionally, can help in the design of products and packaging, making them more attractive and appealing to consumers.
In the social field, neuromarketing can be used to promote behaviors that are beneficial to society. For example, it can help create more effective awareness campaigns on issues such as public health, road safety or environmental protection. By better understanding how people react to certain messages, you can create communications that encourage positive behaviors, such as quitting smoking, using less plastic, or complying with safety regulations.
In both cases, it allows strategies to be based on scientific data, improving the likelihood of success of campaigns and products. This approach helps create messages that not only attract attention, but also motivate people to take concrete actions.
Examples of Neuromarketing
McDonald: I’m lovin it!
McDonald’s uses neuromarketing effectively, harnessing the power of colors and strategic product placement on menus. The colors red and yellow, known to stimulate appetite, are widely used in restaurants and advertising campaigns of the fast food chain, creating an environment that increases the desire to consume.
In addition, McDonald’s introduced the concept of ‘menu engineering‘, strategically placing the best-selling and visually appealing products on the menus. This approach not only simplifies customers’ choices, but also encourages them to order the most profitable items for the company.
The smart use of colors and menu design not only captures the attention of customers, but also influences their buying behavior. These strategies demonstrate how McDonald’s is able to use neuromarketing to create an environment and experience that maximizes sales and meets customer needs.

The Walt Disney Company
Through its iconic stories and characters, Disney arouses feelings of magic and belonging that captivate people of all ages. Using the power of emotions, Disney builds a reputation based on the emotional experience of its content.
In recent years, Disney has expanded its reach, addressing relevant social issues such as gender differences, ethnic minorities and issues of inclusion. This approach builds emotional connection and reflects commitment to diversity and equality, aligning with consumer values.
Using engaging storytelling strategies and a focus on emotional experience, Disney demonstrates how neuromarketing can be used to build lasting and meaningful brands that go beyond mere entertainment.

Coca-Cola: Taste the Feeling!
Coca-Cola uses neuromarketing in a targeted way, leveraging users’ five senses to create a unique emotional and sensory bond. First, the distinctive red color of the logo and bottle immediately captures the visual attention of consumers, while the recognizable design of the bottle stimulates the sense of touch, thanks to its sinuous and familiar shape. The unmistakable flavor of Coca-Cola, constantly maintained over the years, satisfies the sense of taste, creating a memorable and fulfilling taste experience. In addition, the recognizable sound of the cap opening and the effervescence of the drink spark your hearing. Finally, Coca-Cola’s distinctive smell complements the multisensory experience, stimulating the sense of smell.
Studies have shown that the brand’s ability to engage users’ senses is crucial to its long-term loyalty and success. This approach underscores the importance of neuromarketing in creating an authentic and long-lasting brand experience that speaks directly to consumers’ desires and emotions.
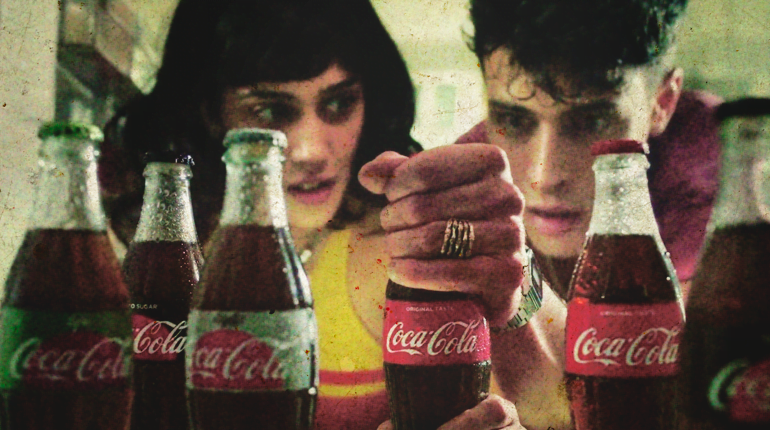
Conclusion
Neuromarketing represents a revolution in the way companies understand and influence their customers. Through the use of neuroscience, you can gain a deeper and more accurate view of consumer behavior, enabling the creation of more effective and targeted marketing strategies.
With a responsible approach, neuromarketing can continue to be a valuable tool for improving consumer experiences and business success.




